Intel Amends CHIPS Act Deal, Secures $5.7 Billion Early From U.S.
Intel successfully renegotiated its CHIPS Act funding agreement, securing an immediate $5.7 billion cash injection from the U.S. government while giving the government a significant equity stake. This landmark deal marks a major shift in how government technology funding operates, moving from traditional grants to equity investments.
The amended deal provides Intel with crucial liquidity during a challenging period for the semiconductor giant. Combined with additional funding sources, the company expects to raise approximately $13 billion this quarter, positioning it to better compete in the rapidly evolving chip industry.
Deal Structure and Financial Terms
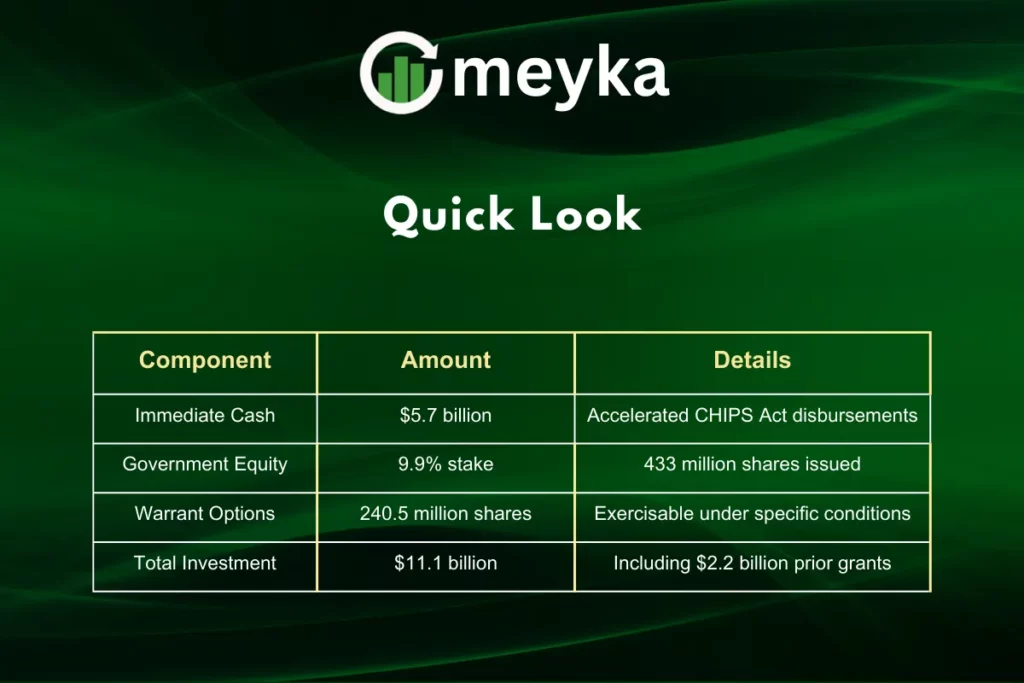
The renegotiated CHIPS Act agreement represents a fundamental change from traditional government grants to equity-based funding. Intel received $5.7 billion in accelerated disbursements on August 29, 2025, with the government acquiring approximately 433 million new shares.
Eliminated Restrictions and Guardrails
The amended agreement removes several key restrictions that previously governed Intel’s use of CHIPS Act funds. These changes provide the company with greater operational flexibility while maintaining some oversight mechanisms.
Removed Requirements:
- Project milestone achievements for fund disbursements
- Sharing percentage of free cash flow with the Department of Commerce
- Most workforce policy requirements
- Government ability to reclaim $2.2 billion in previously paid subsidies
Remaining Restrictions:
- Prohibition on using funds for dividends or share buybacks
- Restrictions on change of control transactions with prohibited entities
- Limitations on semiconductor manufacturing expansion in certain foreign countries
Stock Market Impact and Performance
Intel stock experienced notable volatility following the CHIPS Act deal announcement. The stock market reaction reflected mixed investor sentiment about the dilutive nature of the government equity investment.
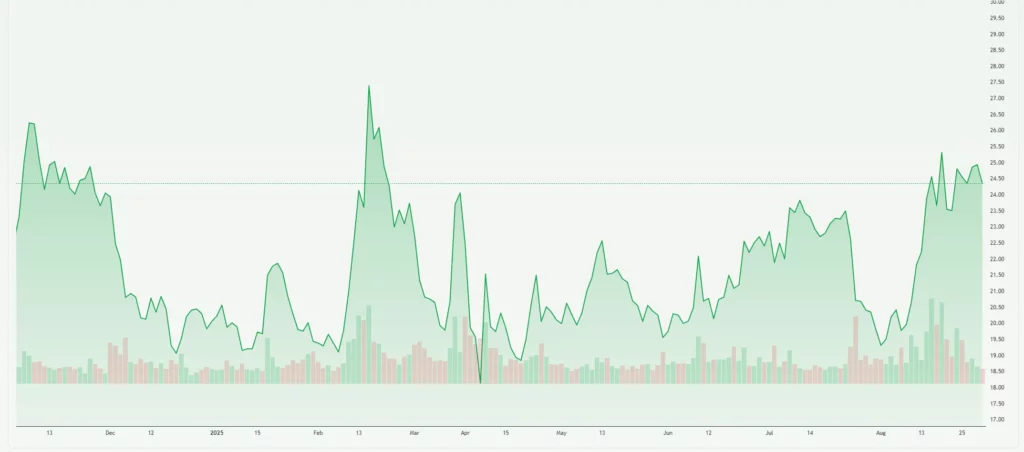
Between August 25-30, 2025, Intel shares declined 4.51%, closing at $24.35 on August 30. The stock opened at $25.50 on August 25 and reached a weekly high of $25.88 before trending downward. Trading volume averaged approximately 90 million shares during this period, indicating heightened investor interest.
The government’s 9.9% equity stake makes it potentially Intel’s largest shareholder, which could influence future strategic decisions and stock market performance. Investors expressed concerns about dilution from the new share issuance and potential limitations on future transactions.
Strategic Implications for Intel’s Business
The CHIPS Act amendment positions Intel to pursue its foundry business expansion while maintaining domestic semiconductor manufacturing capabilities. The company committed to retaining at least 51% ownership of its foundry division for five years, ensuring continued control over this strategic business segment.
Intel’s finance chief David Zinsner confirmed the company’s broader fundraising efforts, expecting total quarterly funding of $13 billion. This includes $2 billion from SoftBank, $1 billion from partial Mobileye sales, and $3.5-4.5 billion from the upcoming Altera partial sale.
The deal provides Intel with financial stability during its transformation from primarily a CPU manufacturer to a comprehensive foundry services provider. This shift becomes increasingly important as the company competes with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company and other contract manufacturers in the global stock market.

Government Oversight and Voting Rights
The amended agreement establishes specific governance structures for the government’s equity position in Intel. The Department of Commerce must vote its shares according to Intel’s board recommendations, except in specific circumstances involving violations or material adverse impacts.
The government retains voting independence for decisions regarding:
- Actions that would violate the purchase agreement
- Proposals to terminate the government relationship
- Matters that would impact Intel’s ability to comply with its obligations
These provisions balance government investment protection with Intel’s operational autonomy, addressing concerns about potential interference in business decisions that could affect stock market performance.
Industry Context and Competition
Intel’s CHIPS Act deal occurs amid intense competition in the semiconductor industry, particularly from NVIDIA’s dominance in artificial intelligence chip markets. The funding provides Intel with resources to accelerate domestic chip manufacturing and reduce U.S. dependence on foreign semiconductor production.
The agreement supports broader U.S. strategic goals of reshoring critical technology manufacturing. Intel’s poured $7.87 billion into projects eligible for CHIPS Act funding, showing real strides in boosting U.S. semiconductor production.
This government investment reflects recognition of Intel’s strategic importance to U.S. technology infrastructure and national security interests, influencing both Intel’s position and broader stock market sentiment toward domestic semiconductor companies.
Disclaimer:
This content is made for learning only. It is not meant to give financial advice. Always check the facts yourself. Financial decisions need detailed research.






