Nippon Steel Notes Minor Differences With US on Golden Share Issue
On June 18, 2025, Nippon Steel bought U.S. Steel for $14.9 billion. This is a big change in the global steel market. The deal included a special “golden share” held by the U.S. government. A golden share is different from normal shares. It gives the holder the power to stop certain company decisions. The U.S. president can block plant closures, moves, or big business deals by U.S. Steel.
Nippon Steel said it is committed to the U.S. market. It also accepts that the U.S. government can step in when needed. But both sides see the golden share rules in slightly different ways. This shows how tricky it is to balance national security and company freedom. Knowing these details is important to understand how this deal will affect Nippon Steel and the U.S. steel industry in the long run.
Background on Golden Shares
A golden share is a special type of stock. It gives the holder extra power to stop certain company decisions. The holder usually owns very little of the company. Unlike regular shares, it does not give dividends or profits. Instead, it gives control over important decisions, like mergers, acquisitions, plant closures, or moving operations. Governments often use golden shares to protect industries that are important for national security or the economy.
In the U.S. Steel deal, the U.S. government holds the golden share. This allows the president to block actions like closing factories, changing the company name or headquarters, and moving jobs or production overseas. Even though Nippon Steel owns most of the company, some key decisions stay under U.S. control. This shows how important the steel industry is for U.S. national security.
Nippon Steel’s Current Situation
Nippon Steel, Japan’s largest steel company, bought U.S. Steel for $14.9 billion on June 18, 2025. This was part of a plan to grow globally and improve technology. U.S. Steel will keep its name and headquarters in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. An American CEO will lead it, and most of the board will be U.S. citizens. Nippon Steel also promised to invest about $11 billion in U.S. Steel by 2028. This includes big upgrades to plants in Pennsylvania and Indiana.
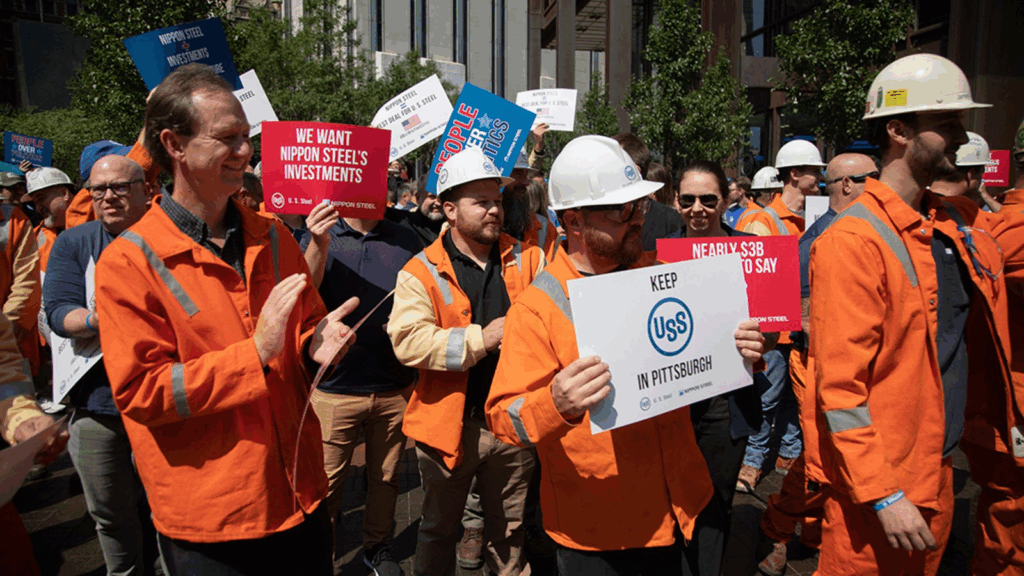

Even with these plans, a small disagreement came up with the U.S. government. It is about how much power the golden share gives. Nippon Steel President Tadashi Imai said there is a “minor difference in views” on national security rules and the golden share’s limits. The company is still committed to the U.S. market and its workers. But this shows how tricky it is to balance company control with national security rules.
U.S. Regulatory Perspective
The U.S. government used the golden share in the Nippon Steel deal. This shows a trend of more rules on foreign investments in important industries. The golden share lets the government watch over decisions that affect national security, even if a foreign company owns most of the business. For example, the Trump administration used the golden share to stop U.S. Steel from closing its Granite City, Illinois, plant, citing security concerns.
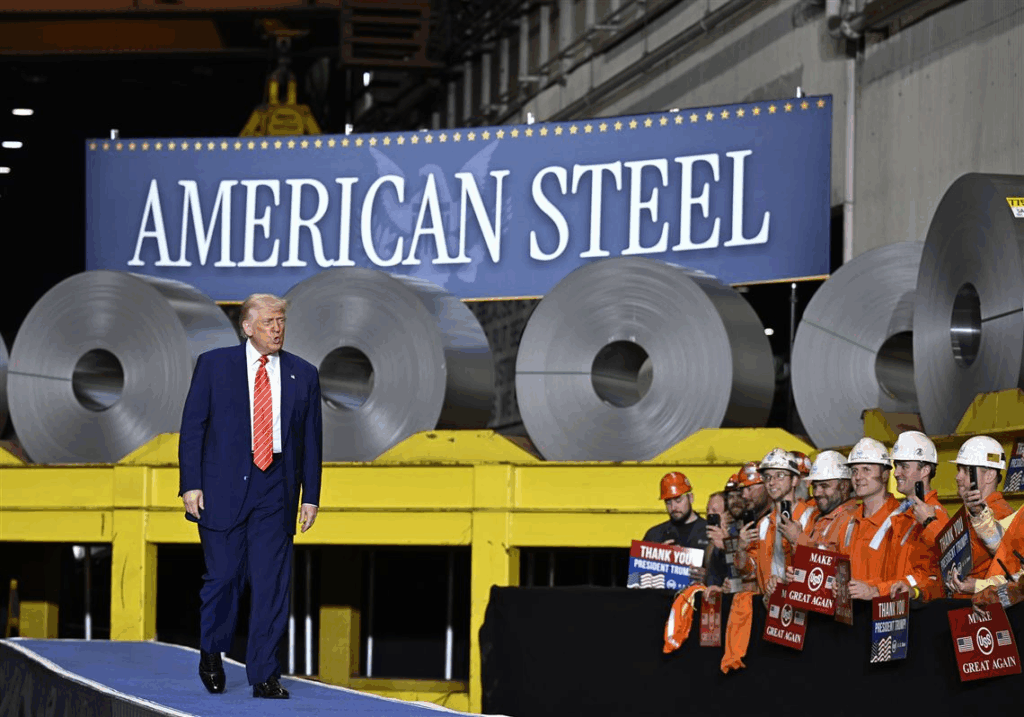
This shows that the U.S. wants to protect its factories and jobs in key sectors. By keeping veto power, the government makes sure foreign ownership does not hurt the industry. But this also creates challenges for foreign companies. They may have limits on how they run operations or make big decisions.
Implications for Nippon Steel
The small differences about the golden share create both problems and chances for Nippon Steel. In the short term, the company may need more talks with the U.S. government. These talks would clarify the golden share’s power. They may cover investment plans, operations, and company rules to address government concerns.
In the long term, this experience could change how Nippon Steel handles deals in other countries. Learning to work with U.S. rules may help in future markets. The company’s promise to invest heavily in U.S. operations shows it wants a strong presence in America. This could make Nippon Steel more competitive around the world.
Industry Context and Competitor Comparison
Golden shares are rare in the United States but more common in Europe. European countries use them in important industries like energy, defense, and telecom. The U.S. Steel deal is a rare example in the U.S. It shows the government is taking a more active role in foreign investments in key industries.

Other steel companies face similar rules in different countries. For example, China’s Baowu Steel Group faced strict checks when it expanded abroad. It had to change its plans to follow local rules and keep good relations with host countries. These cases show how important it is for companies to understand rules in different markets to succeed internationally.
Wrap Up
The small differences between Nippon Steel and the U.S. government about the golden share show how tricky foreign investments can be in key industries. These differences bring challenges but also chances to work together. Companies and governments can talk and align their goals with national security needs.
As the global market changes, being able to handle these issues will be important for companies growing internationally. The results of these talks may set rules for future foreign investments in the U.S. They could affect how much control companies have over national security concerns.
Disclaimer:
The above information is based on current market data, which is subject to change, and does not constitute financial advice. Always do your research.