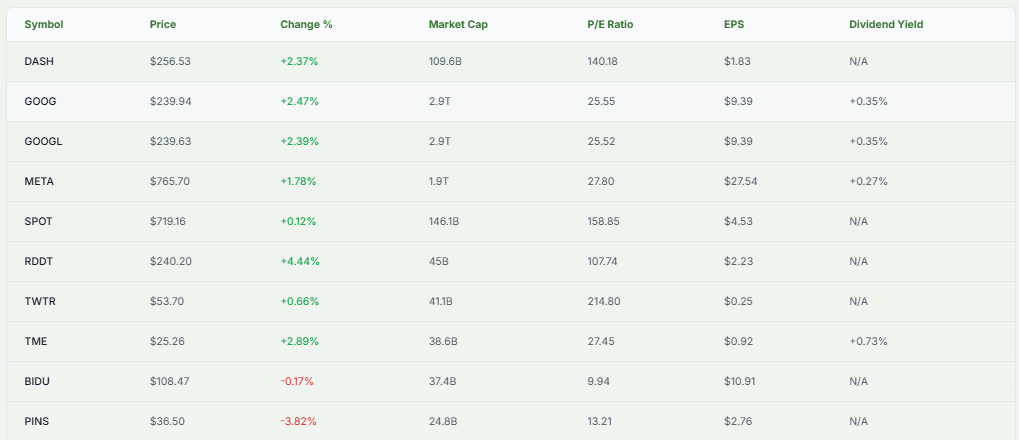
DASH Gains From Autonomous Delivery Despite Fierce Competition
Autonomous delivery is no longer science fiction. We see robots on sidewalks and drones in the sky, carrying food and packages faster than ever. This change is reshaping how we think about speed, safety, and convenience. The market for autonomous delivery is projected to grow rapidly, crossing billions in value within this decade.
In this space, DASH has started to make its mark. While big names like Amazon, Uber, and Walmart are leading experiments, DASH is carving its own path. It focuses on smart technology, customer trust, and efficient delivery systems. We all know competition is tough, but innovation often comes from those who stay agile.
Why does this matter? Because last-mile delivery is the costliest part of logistics. Automation reduces costs, improves timing, and creates new business opportunities. As customers, we want quick, reliable, and safe service. DASH knows this and is betting big on autonomous solutions.
This article looks at how DASH is gaining ground despite strong rivals. We will explore the rise of autonomous delivery, the challenges, and how DASH plans to stand tall in a crowded market.
The Rise of Autonomous Delivery
Autonomous delivery moved from labs to streets in recent years. Sidewalk robots, street-legal pods, and drones now run trials in many cities. These systems cut last-mile costs and speed up deliveries. Retailers and restaurants test robots for short trips and drones for longer, fast drops. Regulation and public acceptance still shape the pace of rollout. Industry reports show dozens of active pilots and growing investment in robotics and drone firms.
DASH’s Position in the Market
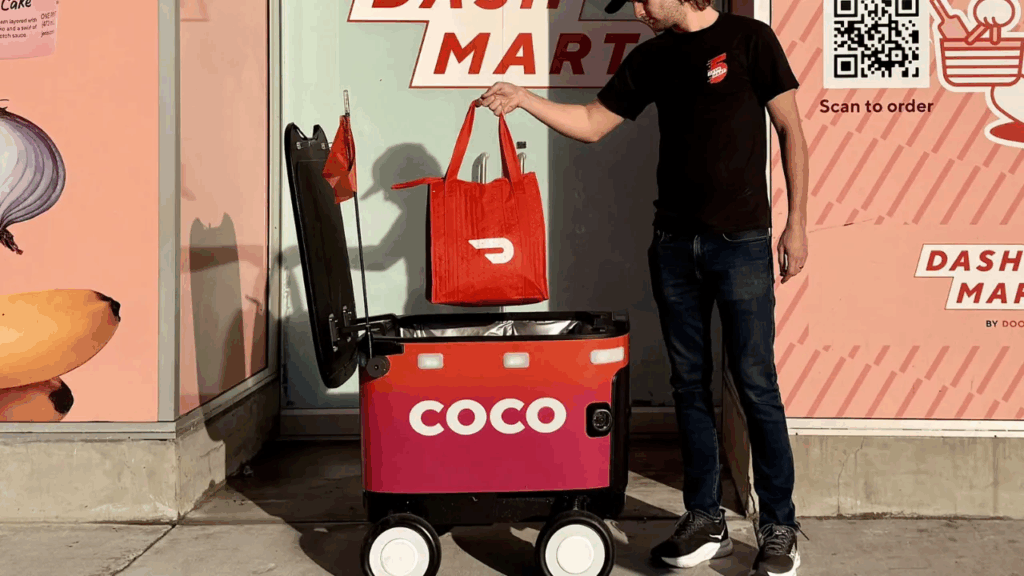

DoorDash (ticker: DASH) is shifting from pure app delivery to a multi-modal platform. The firm added robot delivery to its options through a partnership with Coco Robotics. This program launched in Los Angeles and Chicago after trials abroad. DoorDash also works with drone operators such as Wing and Flytrex on limited pilots. The company keeps DashMart and partner stores as key fulfillment sources for autonomous runs. These moves show intent to mix human drivers with machines for last-mile work.
Competitive Landscape
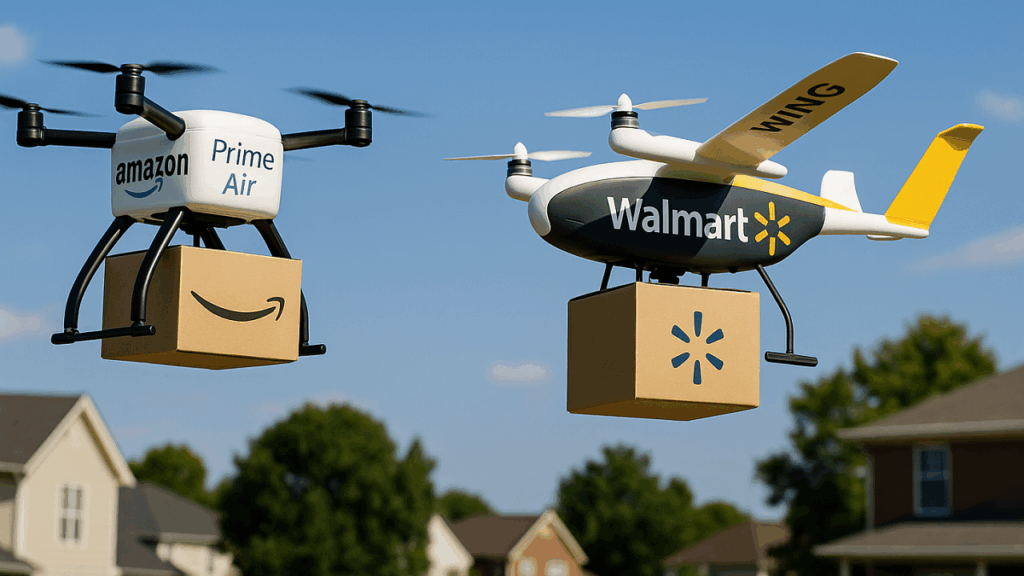

Major rivals push similar tech. Amazon invests in drones and has a large logistics base. Walmart expands drone and in-store automation. Uber Eats and other platforms test sidewalk robots and autonomous vans. Many startups build specialized robots and service models. Large players can spend heavily on hardware, regulation, and scaling. Smaller firms and startups focus on niche use-cases or local runs. This split creates many experiments and varying outcomes across cities and countries.
How DASH Gains an Edge?
DoorDash uses a mixed approach. The app links human couriers, robot partners, and drone pilots. This allows flexible routing and lower costs for short deliveries. The Coco robot program targets urban sidewalks and quick convenience runs. Drone trials focus on very fast drops in suburban or low-density zones.
DoorDash also routes orders from DashMart and select merchants to match the right mode. That reduces empty miles and speeds up small-item delivery. Loyalty programs and merchant tools keep restaurants and stores engaged. Together, these parts aim to deliver faster at a lower cost than single-mode systems.
Challenges and Risks
Autonomous delivery faces many hurdles. Rules vary by city, state, and country. Robots must navigate crowds, weather, and traffic. Drones need safe flight corridors and landing zones. Vandalism and theft are real problems in public spaces. High upfront costs exist for hardware, software, and monitoring teams. Public trust matters. Customers and local communities need to accept machines on sidewalks and in neighborhoods. Finally, rivals with deeper pockets can push fast into key markets. These factors slow national scale-up.
Financial and Strategic Growth
DoorDash shows revenue gains from core marketplace services. Investment in autonomous pilots is part of a longer play to cut marginal delivery costs. Robot and drone pilots are cheaper than full-brick infrastructure but still need staff for oversight. Partnerships let DoorDash spread costs and test business models faster. Investors watch cash flow, take rates, and margins tied to delivery costs. Strategic deals and selective investments may improve margins over time if tech scales and regulators cooperate. Recent press shows steady expansion of robot and drone pilots in U.S. cities.
The Future of Autonomous Delivery and DASH
Robots and drones will likely handle many small orders in certain zones. Human drivers may still serve complex or large orders. Multi-modal routing software will decide the best mode for each order. Data on customer wait time and cost per delivery will guide expansion. If regulation becomes clearer, scale could pick up fast. DoorDash’s multi-partner approach keeps options open. Continued pilots, merchant integration, and customer acceptance are key to success. The long view points to a hybrid network where machines reduce cost for short runs and humans tackle edge cases.
Final Words
Autonomous delivery is no longer a distant idea. It is becoming a real part of logistics, with robots and drones changing how goods move. DoorDash has placed itself in the race by mixing human couriers with smart machines. The path is not free of risks. Rules, costs, and competition remain hard tests. Yet, the firm’s flexible model and partnerships give it a chance to grow. The future will not be machines alone but a blend of people and technology. DoorDash aims to make that mix work at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes. DoorDash started robot deliveries with Coco in Los Angeles and Chicago in 2022. It also tested drone delivery with Wing and Flytrex in 2023.
The main challenges include changing rules, high setup costs, weather issues, and public trust. Companies like Amazon, Walmart, and DoorDash face these problems in 2024.
Disclaimer:
The above information is based on current market data, which is subject to change, and does not constitute financial advice. Always do your research.






