F5 Inc. Data Breach Blamed on China Sparks ‘Catastrophic’ Cybersecurity Concerns
In October 2025, the tech world was shaken when F5 Inc., a major cybersecurity and application security provider, confirmed a massive data breach. The attack was quickly linked to state-backed hackers from China, raising alarms across governments and global enterprises. This was not just another cyber incident, it targeted the very company trusted to protect critical networks, banks, and cloud systems.
Experts called it “catastrophic” because F5’s products sit at the core of digital security infrastructure. If attackers broke through F5, they might also access its clients’ systems, creating a domino effect across multiple industries.
This breach exposed the growing reality of cyber warfare, where sensitive data is more valuable than weapons. It also forced the world to ask hard questions: How secure are our defense layers? Can we trust the companies that protect us?
As investigations continue, the F5 incident is becoming a global wake-up call. It proves that no organization is untouchable and that the next big threat may already be inside the network.
Background on F5 Inc.
F5 Inc. builds software and hardware that sit in front of many big networks. Its BIG-IP product manages web traffic and helps stop attacks. Many banks, cloud providers, and governments use F5 technology. The company is widely viewed as a core vendor for application delivery and security.
Timeline of the Data Breach
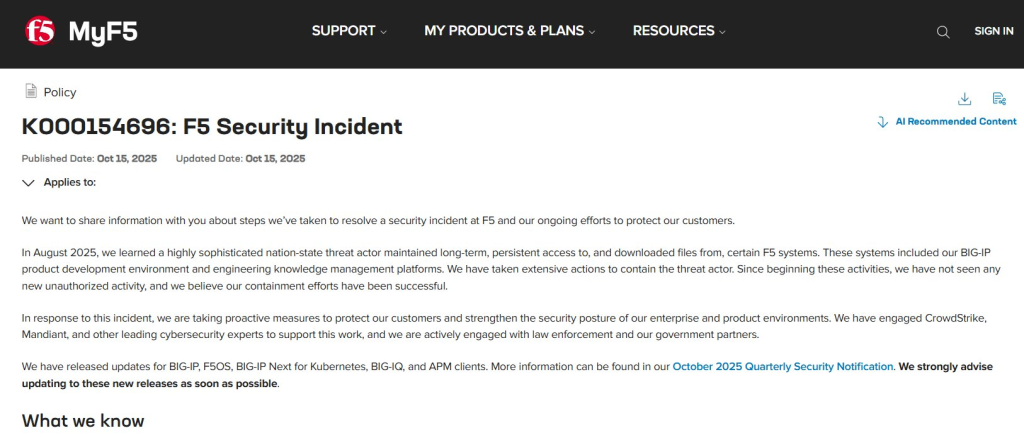
F5 first detected suspicious activity in August 2025. An SEC filing says the company discovered the intrusion on August 9, 2025. The unauthorized access then appears to have continued for many months. Public alerts and federal directives were issued in mid-October 2025.
Who Is Blamed? Allegations Against China
U.S. officials and reporting point to a nation-state actor linked to China. Several news outlets and security sources say the attack profile matches state-backed groups. F5 has described the actor as “highly sophisticated,” though the company has not publicly named a specific group. Diplomatic channels have reacted, and the Chinese embassy has not accepted blame in public statements available so far.

How the F5 Inc., Breach Happened?
Attackers gained persistent access to parts of F5’s engineering and development systems. The files taken include portions of source code and internal notes about vulnerabilities. Access to that material can show flaws in products and give attackers concrete means to target customers. Public reporting suggests attackers used long-term footholds rather than a single short exploit. The exact initial entry is still under investigation.
What Data Was Compromised?
Files tied to the BIG-IP product were among the stolen items. Portions of proprietary source code were taken. Information describing undisclosed vulnerabilities was also exfiltrated. Customer credentials and direct customer systems have not been publicly confirmed as stolen, but the risk to customers is high because stolen code can reveal attack paths.
Why Experts Call It “Catastrophic”?
BIG-IP sits at the network edge for many organizations. If attackers learn how to bypass protections or exploit a device remotely, that gap can affect many customers at once. Security teams say a breach at a core vendor is different from a breach at an ordinary company. A vendor breach can turn a trusted tool into an attack vector for many networks. This broad risk is why experts warned of potentially “catastrophic” consequences in mid-October 2025.
Global Cybersecurity Implications
A supply chain attack on a major security vendor changes the threat landscape. Other vendors will face renewed scrutiny. Governments will push for faster patch cycles. Firms that depend on F5 must assume they are at elevated risk until full analysis is complete. Allies and partners are likely to share more threat intelligence. The incident also stresses the limits of perimeter defenses and highlights the need for layered security.
Legal and Regulatory Response
U.S. agencies stepped in quickly. On October 15, 2025, CISA issued an emergency directive asking federal civilian agencies to catalog and patch affected F5 products. Regulators will review whether disclosure rules were followed. Lawsuits and class actions are likely given the scope of the incident. Foreign agencies, including the UK National Cyber Security Centre, also published guidance.
Data Breach Impact on F5 Inc.
F5’s leadership began direct briefings with customers in October 2025. The company said operations were not disrupted, but it acknowledged data exfiltration. Investors and analysts will re-price risk to F5 based on potential client churn and legal exposure. Some market researchers will run scenario models. An AI stock research analysis tool may be used by analysts to estimate short-term stock moves and longer-term damage.
Lessons Learned from the Incident
Relying on a single vendor for critical defenses creates concentration risk. Companies must adopt zero-trust principles and segment networks. Regular audits of vendor access and code custodianship are essential. Rapid patching and emergency playbooks must be in place. Transparency and timely disclosure help clients respond faster.
Industry Reactions
Security firms urged customers to apply emergency fixes. Competitors revisited their own architectures and communications. Insurance carriers began to reassess cyber policies tied to supply-chain incidents. Corporate boards asked CISOs for proof of vendor-risk management and contingency plans. Public-private partnerships are likely to expand to handle cross-industry fallout.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices
Patch known vulnerabilities immediately. Verify vendor claims with independent scans. Use multi-factor authentication for engineering tools and developer portals. Limit production and source code access to need-to-know personnel. Prepare incident response playbooks that assume vendor compromise. Regularly test backup and recovery under adversary conditions.
The Future of Cybersecurity in 2025 and Beyond
State-backed campaigns will remain a top threat. Expect more emergency directives like the October 15, 2025 CISA order. Encryption, stronger code guardianship, and automated detection will grow in importance. Talent shortages will push organizations to combine human experts with AI tools for threat hunting. International cooperation on norms and responses will also rise.
Wrap Up
The F5 data breach changed the conversation about vendor risk. The incident exposed how a single breach can ripple across industries. Firms must act fast to patch and to harden defenses. The October 2025 disclosures showed that even trusted security vendors can be targets. The path forward requires faster sharing, better vendor controls, and stronger global cooperation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In October 2025, F5 Inc. confirmed hackers accessed internal systems and stole source code and security data, raising major risks for customers using F5 products.
U.S. officials and reports suggest a state-backed group from China may be responsible, but F5 has not confirmed any specific country or attacker as of October 2025.
The breach could expose hidden flaws in BIG-IP devices, allowing hackers to target company networks. Users must apply patches and follow security updates to stay safe.
Disclaimer: The above information is based on current market data, which is subject to change, and does not constitute financial advice. Always do your research.