Halloween Cocoa Prices Drop, Sweet News for Chocolate Stocks
This year’s Halloween season brings a welcome relief for candy manufacturers thanks to a drop in cocoa prices, and the mood is improving for chocolate-based snack makers and investors alike. The term “Halloween cocoa” captures the seasonal surge in cocoa demand tied to Halloween candy production. With cocoa supply concerns easing and input costs falling, companies in the confectionery sector may see stronger margins ahead.
For those interested in the stock market, including thematic sectors like AI stocks or consumer goods, this development merits attention.
What’s Driving the Cocoa Price Drop
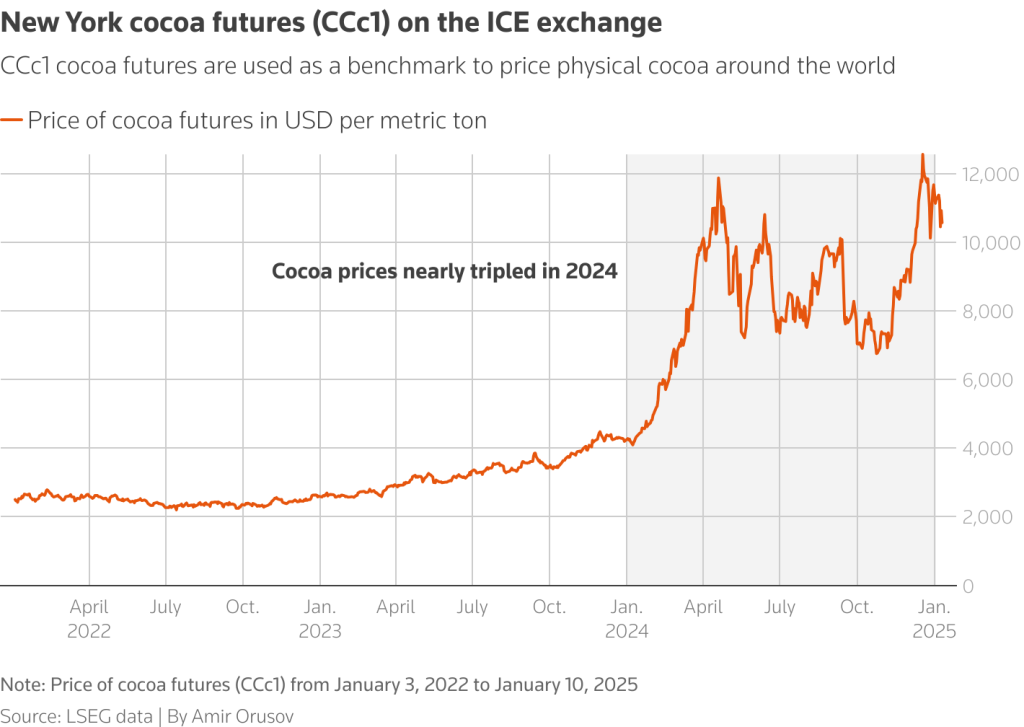
After a period of severe supply constraints and record highs, cocoa prices have started to fall. According to an analysis by eToro, cocoa prices are down approximately 51% this year from the highs driven by raw-material shortages and weak demand. The decline is also visible in futures data: cocoa futures recently traded near US$6,100 per tonne, easing from earlier peaks.
Key factors behind the drop include:
- Improved supply in major producing countries in West Africa, reducing the pressure on inventories.
- Weaker demand for chocolate in some regions, impacting cocoa grindings. For example, the Q3 European cocoa grindings fell nearly 5% year-on-year.
- Higher inventory levels and less speculative pressure in the cocoa futures markets.
For the Halloween cocoa context, the drop means that the cost of making seasonal chocolate treats may be less elevated than in previous years, supporting confectionery makers.
Implications for Chocolate Stocks and Stock Research
For investors practicing sound stock research, the cocoa price reduction has several implications:
- Improved margins: Chocolate producers spend a significant portion of their costs on cocoa. When prices ease, margin pressure relents. The eToro report shows confectionery stocks inching up about 14% year-to-date as margins recover.
- Sector rotation opportunities: While much of the market buzz today is around technology and AI stocks, some value lies in traditional consumer goods, especially when input cost headwinds fade.
- Risk/reward balance: The chocolate sector carries its own risks, including consumer demand shifts, packaging costs, and brand competition. But the commodity relief adds a favourable tailwind.
- Broader stock market context: With commodity-driven inflation easing, cyclical sectors like food & beverages may benefit. This could influence portfolios that have been heavily oriented toward high-growth themes like AI.
If you track confectionery companies (for example, The Hershey Company or Mondelez International), this cocoa cost dynamic is a key part of their cost structure and future earnings outlook.
Why the Drop Matters for Halloween Candy
Halloween accounts for a high share of the annual candy demand. Chocolate bars and seasonal packs often see heightened production ahead of the trick-or-treat rush. With input costs falling, manufacturers may choose to stabilise retail prices or maintain product sizes, which can help consumer demand.
Moreover, consumer taste is shifting. In recent data, chocolate candy volumes fell roughly 13.7% in the U.S. for the 12 weeks ahead of early October, while non-chocolate candies rose 4.5%. Lower cocoa prices may help chocolate makers fight back and regain share.
Therefore, the term “Halloween cocoa” emphasises how this seasonal theme matters not only to candy makers but also to commodity markets and stock-market watchers.
Challenges and Caveats Ahead
Even with the positive trend, several caveats should be kept in mind for investors and market observers:
- Demand uncertainty: While input costs are down, if consumer demand for chocolate remains weak (or shifts further to alternatives like gummies), the benefit of cheaper cocoa may not fully translate into stronger earnings. For example, a recent article noted chocolate-candy sales volume in major markets.
- Volatility remains: Although prices dropped, the cocoa market remains subject to risks like weather in West Africa, crop disease, and geopolitical disruption. These factors could quickly reverse the cost relief.
- Competitive market and margin pressure: Even if costs decline, companies may not pass all savings to the bottom line due to packaging, labour, and other overhead costs.
- Stock market valuations: Confectionery stocks are not immune to equity-market shifts. For those drawn to high-growth sectors like AI or tech, the consumer goods sector may seem less exciting unless execution is strong.
What to Watch: Key Metrics and Upcoming Catalysts
If you’re doing stock research or simply monitoring this trend, here are metrics and events to keep an eye on:
- Cocoa futures: Track contracts (e.g., ICE Cocoa futures) and inventory levels, since these influence cost trends.
- Company earnings reports: Look at chocolate makers’ earnings releases that include comments on raw-material costs, especially cocoa.
- Halloween / seasonal candy sales: Companies often give forward guidance around holiday seasons; stronger sales may indicate demand resilience.
- Margin improvement: Watch whether cost relief actually translates into gross-margin expansion for firms in the confectionery space.
- Macro factors: Weather in cocoa-growing regions, trade policy (tariffs on cocoa beans), and currency moves can all impact the input cost.
- Stock market sentiment: General equity-market risk appetite impacts all sectors, including consumer goods.
Conclusion
In summary, the drop in cocoa prices has brought an unexpectedly sweet twist to the Halloween candy season and has meaningful implications for the chocolate sector. The theme of Halloween cocoa underlines how commodities and consumer cycles still matter deeply in an era dominated by stories of AI stocks and tech disruption.
For investors who perform solid stock research, the reduction in cocoa input costs suggests potential upside for chocolate producers if demand recovers. As always, risks remain, but the current environment offers a compelling backdrop in the consumer goods arena.
FAQs
Cocoa prices dropped primarily due to improved supply dynamics in major producing regions and weaker demand in some key markets. According to eToro, prices fell about 51% year-to-date from recent highs.
Lower cocoa prices reduce one of the largest input costs for chocolate manufacturers. That can improve profit margins, potentially boost earnings, and make companies more attractive in the stock market. For investors doing stock research, companies with strong brands and cost control may benefit the most.
Not necessarily. While cost pressures are easing, demand remains uncertain. Consumer preferences may shift toward non-chocolate treats or cheaper options. Companies will need to execute marketing, pricing and packaging strategies effectively to translate cost relief into increased sales. Evidence already shows chocolate volumes falling in recent weeks.
Disclaimer:
The content shared by Meyka AI PTY LTD is solely for research and informational purposes. Meyka is not a financial advisory service, and the information provided should not be considered investment or trading advice.






