India’s wholesale prices fall 0.32% year-on-year in November
In November 2025, the Indian wholesale price index (WPI) showed a 0.32% decline year-on-year, meaning average prices at the wholesale level were lower than in November 2024. This data was released on December 15, 2025, by the government. The drop is smaller than the 1.21% fall seen in October, showing that prices are still easing, but the pace of decline has slowed.
Wholesale prices matter. They show early trends in the cost of goods before they reach shops.
A fall in WPI can signal weaker price pressure in the economy. It can affect business margins, government policy, and interest-rate decisions. This makes the November print important for economists and market watchers alike.
In simple terms, this number hints at how costs are moving for producers and traders. It also gives an early clue about inflation pressures felt by consumers later.
India Wholesale Price Index: How It Differs from CPI?
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) shows price changes at the wholesale level before goods reach shops. It tracks prices for raw materials, fuel, power, and manufactured goods. WPI and Consumer Price Index (CPI) both measure inflation, but they serve different purposes. CPI shows price change as seen by consumers. WPI reflects cost pressures for producers and traders. Economists watch WPI closely because it can signal future trends in CPI.
A fall in WPI often points to weaker cost pressure in the production chain. This can reduce inflation pressure at retail stores later. WPI also helps businesses plan pricing, budgets, and contracts based on cost trends before consumer prices shift.
November 2025 WPI Breakdown: Sector-Wise Performance
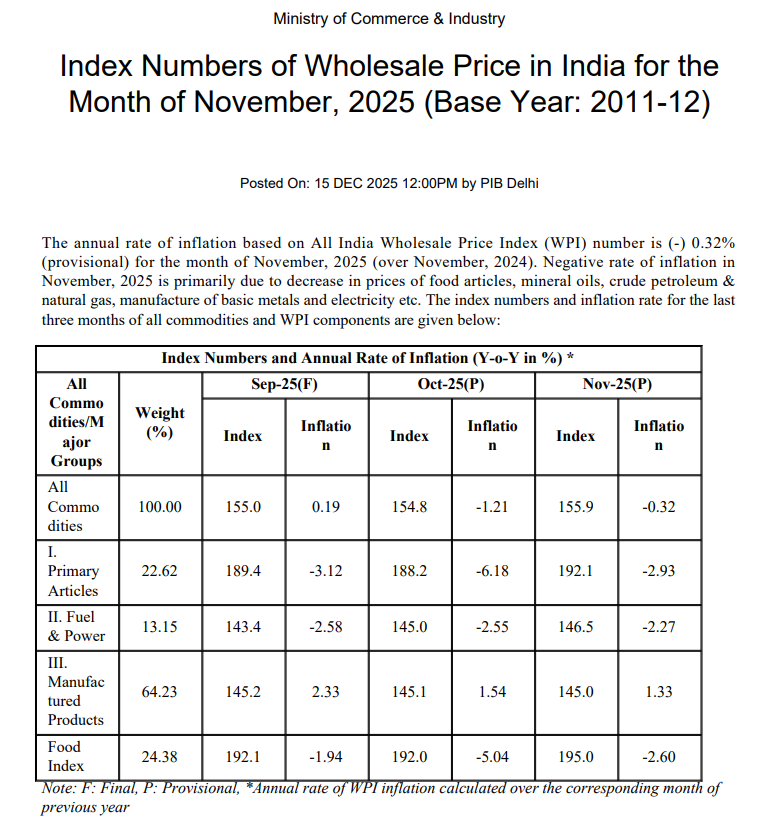
India’s WPI in November 2025 stayed in deflation at -0.32% YoY, improving from a -1.21% drop in October. This means prices are still falling, but not as fast as before.
Primary Articles & Food: Food prices stayed in deflation, with a sharp drop in food WPI far below last year’s figures. This was led by cheaper vegetables, pulses, cereals, and fruits at the wholesale level.
Fuel & Power: Fuel and power costs continued to ease, reflecting lower energy costs and stable global crude oil prices. This kept the overall index down.
Manufactured Products: Prices of goods made in factories rose moderately but at a slower pace than before. This shows core manufacturing costs are still increasing, though less strongly than in earlier months.
Key Drivers Behind the 0.32% YoY Decline
Several forces pushed the WPI into negative territory:
Food Price Deflation: Wholesale food prices continued to slide sharply. This was one of the main reasons the overall index stayed below zero.
Fuel and Energy Trends: Lower costs for mineral oils, electricity, and other fuels kept the WPI down. These costs feed into production and transport, so they matter for overall pricing.
Base Effect: Last year’s higher base means even small declines this year can look larger in percentage terms. This can distort trend interpretations for a short period.
Core Goods Moderation: Although manufactured product prices remain positive, they rose more slowly than in earlier months. This reduced upward pressure on WPI.
What Negative WPI Means for Indian Businesses?
A falling India Wholesale Price Index shows that producers are paying less for inputs. This can help business margins if sales prices remain stable. Lower input cost often reduces production expenses for food processors, manufacturers, and traders.
However, it also points to weak pricing power. Firms may struggle to raise prices if demand is slow. Cheap inputs can be good for sectors like consumer goods and construction. But if demand stays weak, companies may hold back investments until pricing strength returns. Exporters may gain a small boost. Lower domestic cost pressure can make Indian goods more competitive abroad. But global demand also shapes export performance.
Impact on Retail Inflation (CPI): Signal or False Alarm?
WPI trends often lead CPI trends. If producers face lower costs, retail prices might fall later as goods move down the supply chain. But the link isn’t always strong or immediate. CPI covers services and items not fully captured in WPI, like housing and healthcare.
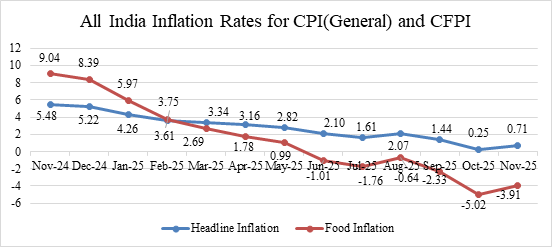
Recent CPI data showed a slight rise to 0.71% in November 2025, though it stayed well below the RBI’s target range. This rise was due to slower declines in food prices at the retail level.
So, while wholesale deflation points to weaker inflation pressure, retail figures can diverge due to factors like services inflation and consumer demand.
RBI Policy Implications: Rate Cuts or Wait-and-Watch?
With WPI in deflation, inflation pressure seems light. This gives the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) room to consider easing monetary policy. RBI has cut rates several times in 2025 to support growth.
The recent drop in inflation data may prompt policymakers to stay accommodative. They could slow future rate hikes or widen the room for cuts if economic growth weakens further.
The next monetary policy committee meeting, likely in early February 2026, will weigh these trends closely alongside retail inflation and growth data.
Market Reaction and Investor Takeaways
Investors watch WPI closely because it affects bond yields and currency markets. A weaker WPI can push bond yields lower as inflation pressure eases. Lower inflation expectations can support longer-term government securities.
Stock markets may react based on sector outlooks. Consumer goods and industrial companies may benefit from lower input costs. But weak pricing power could hurt these sectors if demand falters.
The risk appetite of investors also hinges on global economic cues and domestic demand signals. WPI is one input in a broader data set guiding market direction.
India in Global Context: How WPI Compares Internationally?
Worldwide, producer price indices have varied widely in 2025. Some countries face rising costs due to energy supply shocks, while others see easing pressures as commodity prices stabilize. India’s sustained deflationary trend contrasts with moderate inflation in major economies this year.
This mix of global trends affects trade and competitiveness. Lower Indian wholesale costs can help exporters. But slower global demand can offset this benefit.
Wholesale India Outlook: Is WPI Deflation Temporary or Structural?
The November print appears to be part of a broader trend of easing price pressures in India through 2025. While some sectors show signs of stabilizing, others, like food and energy, remain key drivers of deflation.
Future months will reveal whether this trend holds. Weather patterns, global energy prices, and demand conditions will shape WPI’s direction.
Despite deflation in wholesale prices, a sustained recovery in domestic demand or global price pressures could push WPI back into positive territory. Markets and policymakers will watch these moves closely.
Final Words
India’s wholesale price index fell 0.32% in November 2025, highlighting a continued trend of easing price pressures. This deflation reflects weak cost trends in food and fuel, slower manufacturing price rises, and global commodity stability. While it offers relief to producers, it also signals caution on pricing power and demand. By watching WPI alongside retail inflation and RBI policy decisions, analysts get a clearer picture of India’s economic trend going into 2026.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The India Wholesale Price Index fell in November 2025 due to lower wholesale food prices, softer fuel costs, and slower growth in manufactured goods prices, reducing overall price pressure.
Negative WPI can lower business input costs and ease inflation pressure, but it may also signal weak demand and limited pricing power across industries during slower economic periods.
Lower WPI inflation reduces cost pressure in the economy and can support a softer RBI policy stance, influencing interest rate decisions in upcoming policy reviews after December 2025.
Disclaimer:
The content shared by Meyka AI PTY LTD is solely for research and informational purposes. Meyka is not a financial advisory service, and the information provided should not be considered investment or trading advice.






